Toyohashi Tech and The National Academy of Sciences in Ukraine proposed new curcumin-based agents for protecting against Alzheimer's disease (AD).
The curcumin-based agents can fight Alzheimer's in the following way:
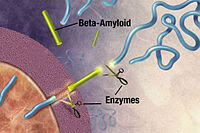
- Alzheimer's is caused by the buildup of beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptides in the brain.
- Blocking production of Aβ can block Alzheimer's.
- Curcumin-based agents were developed by these researchers to suppress production of Aβ
- Aβ was blocked by inhibiting the secretase-mediated cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) into Aβ peptides.
- In summary, the curcumin derivatives protect the cleavage site of APP from attack by γ-secretase.



γ-secretase enzymes (Gamma-secretase enzymes) act on the APP (amyloid precursor protein) and cut it into fragments. These fragments, called beta-amyloid fragments, form the plaques that trigger Alzheimer's.
The simulated results elucidated the specific curcumin derivative and showed that it bound more strongly to APP and inhibited the binding of secretase to APP more than the other derivatives did . Moreover, some novel curcumin derivatives were proposed as potent inhibitors of Aβ peptide production. These derivatives are novel agents for suppressing AD and are proposed based on the novel concept of preventing APP cleavage. However, this does not imply that the consumption of Indian cuisine suppresses AD.
Numerous types of agents have been developed to suppress the production of Aβ, by inhibiting the secretase-mediated cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) into Aβ peptides.
However, because the secretases also play important roles in the production of vital proteins for the human body, inhibitors of the secretases have increased risk for side effects.
The first author, graduate student Hiromi Ishimura said, "We have also been studying the aggregation mechanism of Aβ peptides by using molecular dynamics simulations (Okamoto et al. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modeling, 50, 113-124, 2014; Yano et al. Chemical Physics Letters, 595-596, 242-249, 2014). By combining the present ab initio molecular simulation and the molecular dynamics simulations, we will be able to elucidate the mechanism and propose potent inhibitors for suppressing the aggregation of Aβ peptides. These inhibitors are used as a therapeutic agent for ADs."
Associate Professor Noriyuki Kurita said, "Our present molecular simulations elucidated that curcumin can bind APP and inhibit the cleavage of APP by secretase. Curcumin is a natural product contained in the root of Curcumae Rhizoma. In the laboratory of our collaborator at National Academy of Sciences in Ukraine, our proposed curcumin derivatives will be synthesized and theirs effects on experimental animals with ADs will be investigated."
Reference:
- Hiromi Ishimura, Ryushi Kadoya, Tomoya Suzuki, Takeru Murakawa, Sergiy Shulga, Noriyuki Kurita. Specific interactions between amyloid-β peptide and curcumin derivatives: Ab initio molecular simulations. Chemical Physics Letters, 2015; 633: 139 DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2015.05.023
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology, Toyohashi, 441-8580, Japan,
- Institute for Food Biotechnology and Genomics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
No comments:
Post a Comment
Comment here: